Lehrgebiet: Theoretische Informatik und künstliche Intelligenz
Büro: 01.214
Labor: 04.105
Telefon: +49 208 88254-806
E-Mail:
🛜 http://lab.iossifidis.net

Ioannis Iossifidis studierte Physik (Schwerpunkt: theoretische Teilchenphysik) an der Universität Dortmund und promovierte 2006 an der Fakultät für Physik und Astronomie der Ruhr-Universität Bochum.
Am Institut für Neuroinformatik leitete Prof. Dr. Iossifidis die Arbeitsgruppe Autonome Robotik und nahm mit seiner Forschungsgruppe erfolgreich an zahlreichen, vom BmBF und der EU, geförderten Forschungsprojekten aus dem Bereich der künstlichen Intelligenz teil. Seit dem 1. Oktober 2010 arbeitet er an der HRW am Institut Informatik und hält den Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Informatik – Künstliche Intelligenz.
Prof. Dr. Ioannis Iossifidis entwickelt seit über 20 Jahren biologisch inspirierte anthropomorphe, autonome Robotersysteme, die zugleich Teil und Ergebnis seiner Forschung im Bereich der rechnergestützten Neurowissenschaften sind. In diesem Rahmen entwickelte er Modelle zur Informationsverarbeitung im menschlichen Gehirn und wendete diese auf technische Systeme an.
Ausgewiesene Schwerpunkte seiner wissenschaftlichen Arbeit der letzten Jahre sind die Modellierung menschlicher Armbewegungen, der Entwurf von sogenannten «Simulierten Realitäten» zur Simulation und Evaluation der Interaktionen zwischen Mensch, Maschine und Umwelt sowie die Entwicklung von kortikalen exoprothetischen Komponenten. Entwicklung der Theorie und Anwendung von Algorithmen des maschinellen Lernens auf Basis tiefer neuronaler Architekturen bilden das Querschnittsthema seiner Forschung.
Ioannis Iossifidis’ Forschung wurde u.a. mit Fördermitteln im Rahmen großer Förderprojekte des BmBF (NEUROS, MORPHA, LOKI, DESIRE, Bernstein Fokus: Neuronale Grundlagen des Lernens etc.), der DFG («Motor‐parietal cortical neuroprosthesis with somatosensory feedback for restoring hand and arm functions in tetraplegic patients») und der EU (Neural Dynamics – EU (STREP), EUCogII, EUCogIII ) honoriert und gehört zu den Gewinnern der Leitmarktwettbewerbe Gesundheit.NRW und IKT.NRW 2019.
ARBEITS- UND FORSCHUNGSSCHWERPUNKTE
- Computational Neuroscience
- Brain Computer Interfaces
- Entwicklung kortikaler exoprothetischer Komponenten
- Theorie neuronaler Netze
- Modellierung menschlicher Armbewegungen
- Simulierte Realität
WISSENSCHAFTLICHE EINRICHTUNGEN
- Labor mit Verlinkung
- ???
- ???
LEHRVERANSTALTUNGEN
- ???
- ???
- ???
PROJEKTE
- Projekt mit Verlinkung
- ???
- ???
WISSENSCHAFTLICHE MITARBEITER*INNEN

Felix Grün
Büro: 02.216 (Campus Bottrop)

Marie Schmidt
Büro: 02.216 (Campus Bottrop)

Aline Xavier Fidencio
Gastwissenschaftlerin

Muhammad Ayaz Hussain
Doktorand

Tim Sziburis
Doktorand

Farhad Rahmat
studentische Hilfskraft
GOOGLE SCHOLAR PROFIL

Artikel
Fidêncio, Aline Xavier; Grün, Felix; Klaes, Christian; Iossifidis, Ioannis
Error-Related Potential Driven Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Brain-Computer Interfaces Artikel
In: Arxiv, 2025.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Schlagwörter: BCI, Computer Science - Human-Computer Interaction, Computer Science - Machine Learning, EEG, Quantitative Biology - Neurons and Cognition, Reinforcement learning
@article{fidencioErrorrelatedPotentialDriven2025,
title = {Error-Related Potential Driven Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Brain-Computer Interfaces},
author = {Aline Xavier Fidêncio and Felix Grün and Christian Klaes and Ioannis Iossifidis},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2502.18594},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2502.18594},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-02-25},
urldate = {2025-02-25},
journal = {Arxiv},
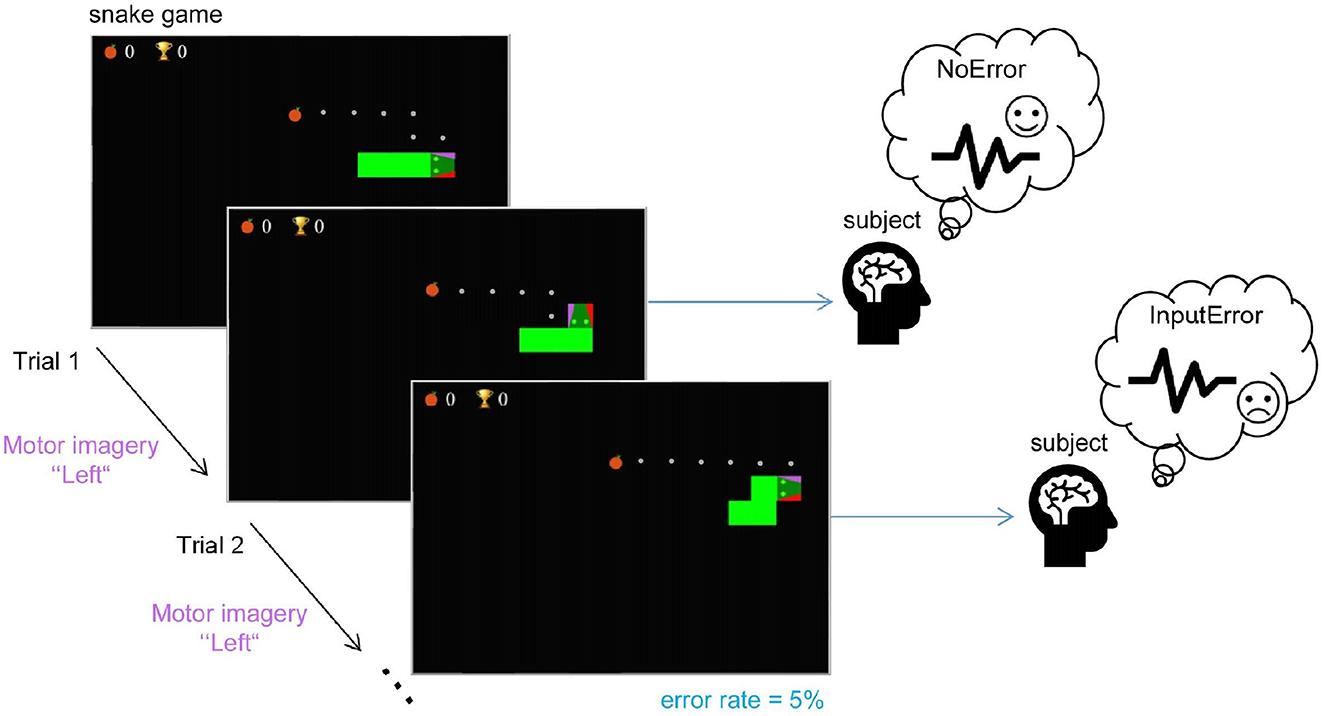
abstract = {Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) provide alternative communication methods for individuals with motor disabilities by allowing control and interaction with external devices. Non-invasive BCIs, especially those using electroencephalography (EEG), are practical and safe for various applications. However, their performance is often hindered by EEG non-stationarities, caused by changing mental states or device characteristics like electrode impedance. This challenge has spurred research into adaptive BCIs that can handle such variations. In recent years, interest has grown in using error-related potentials (ErrPs) to enhance BCI performance. ErrPs, neural responses to errors, can be detected non-invasively and have been integrated into different BCI paradigms to improve performance through error correction or adaptation. This research introduces a novel adaptive ErrP-based BCI approach using reinforcement learning (RL). We demonstrate the feasibility of an RL-driven adaptive framework incorporating ErrPs and motor imagery. Utilizing two RL agents, the framework adapts dynamically to EEG non-stationarities. Validation was conducted using a publicly available motor imagery dataset and a fast-paced game designed to boost user engagement. Results show the framework's promise, with RL agents learning control policies from user interactions and achieving robust performance across datasets. However, a critical insight from the game-based protocol revealed that motor imagery in a high-speed interaction paradigm was largely ineffective for participants, highlighting task design limitations in real-time BCI applications. These findings underscore the potential of RL for adaptive BCIs while pointing out practical constraints related to task complexity and user responsiveness.},
keywords = {BCI, Computer Science - Human-Computer Interaction, Computer Science - Machine Learning, EEG, Quantitative Biology - Neurons and Cognition, Reinforcement learning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}